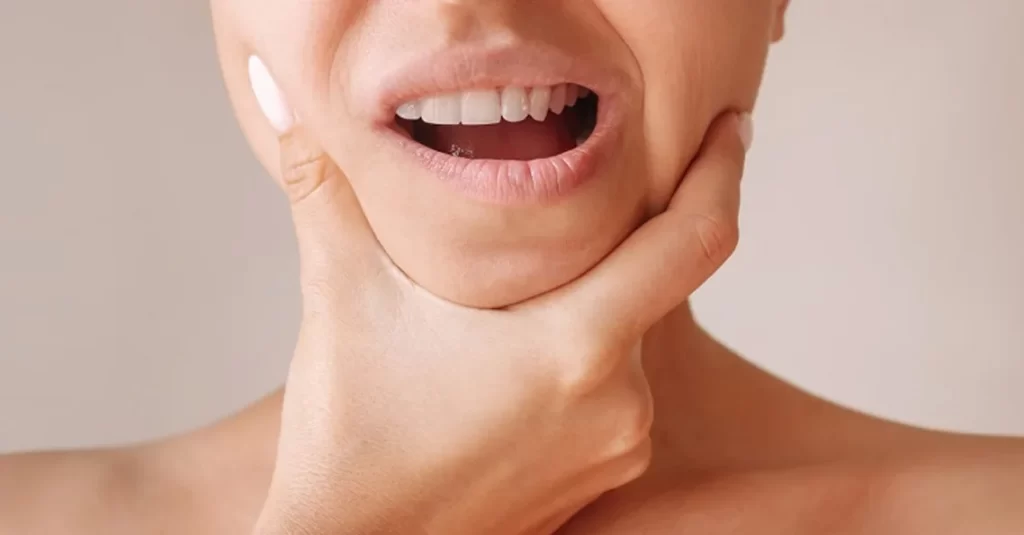
Exploring the intricate relationship between temporomandibular joint (TMJ) pain and headaches reveals a complex puzzle that many individuals grapple with. In this comprehensive guide, we embark on a journey to unravel the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and solutions for TMJ-related jaw pain and headaches, offering insights to empower those seeking relief.
Causes:
1. TMJ Disorders: Dysfunction within the temporomandibular joint, stemming from factors such as injury, arthritis, or structural anomalies, can ignite jaw pain, which often extends to trigger headaches.
2. Bruxism (Teeth Grinding): The habitual clenching or grinding of teeth, typically during sleep, imposes significant strain on the TMJ and surrounding muscles, fostering both jaw pain and headaches.
3. Muscle Tension: Elevated stress levels commonly manifest as heightened tension within the jaw muscles, serving as a precursor to TMJ-related discomforts, including jaw pain and headaches.
Symptoms:
1. Localized Jaw Pain: Persistent discomfort or pain localized within the jaw joint or surrounding muscles is a hallmark symptom of TMJ disorders, hindering everyday activities such as chewing and speaking.
2. Headaches: Headaches, often localized around the temples, forehead, or behind the eyes, frequently accompany jaw pain, varying in intensity and duration, and impacting overall well-being.
3. Clicking or Popping Sounds: Audible clicking, popping, or grating sounds during jaw movement, alongside sensations of jaw locking or limited mobility, indicate underlying TMJ irregularities.
Treatment Options:
1. Lifestyle Modifications: Incorporating stress management techniques, mindful eating habits, and avoiding hard or chewy foods can alleviate TMJ-related symptoms and reduce associated headaches.
2. Oral Appliances: Custom-made mouthguards or splints prescribed by TMJ specialists serve to cushion the teeth, redistribute bite forces, and promote optimal jaw alignment, facilitating relief from jaw pain and headaches.
3. Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises, stretching routines, and manual therapies administered by qualified physical therapists enhance jaw muscle flexibility, strength, and coordination, easing TMJ-related discomforts.
4. Medication: Healthcare professionals may recommend non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or muscle relaxants to alleviate pain, inflammation, and muscular tension associated with TMJ disorders.
Seeking Professional Help:
Individuals experiencing persistent jaw pain, headaches, or TMJ-related symptoms should prioritize seeking assistance from healthcare professionals or dentists specializing in temporomandibular disorders. A comprehensive evaluation, including medical history review and diagnostic imaging, can inform personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs.
Conclusion:
The intricate connection between TMJ, jaw pain, and headaches underscores the importance of holistic management strategies. By understanding the diverse causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can navigate their journey toward relief, enhancing their overall quality of life.
FAQ
Can stress exacerbate TMJ-related symptoms?
Yes, heightened stress levels often manifest as increased muscle tension, worsening TMJ-related discomforts such as jaw pain and headaches.
How long does it take to see improvement with TMJ treatment?
The timeline for improvement varies depending on the severity of the condition and the chosen treatment approach. Some individuals may experience relief within weeks, while others may require several months of consistent treatment to achieve significant improvement.
Are there any exercises I can do at home to alleviate TMJ pain?
Yes, certain jaw exercises, such as gentle stretches and resistance training, can help improve jaw mobility and reduce muscle tension. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist before starting any new exercise regimen to ensure safety and effectiveness.