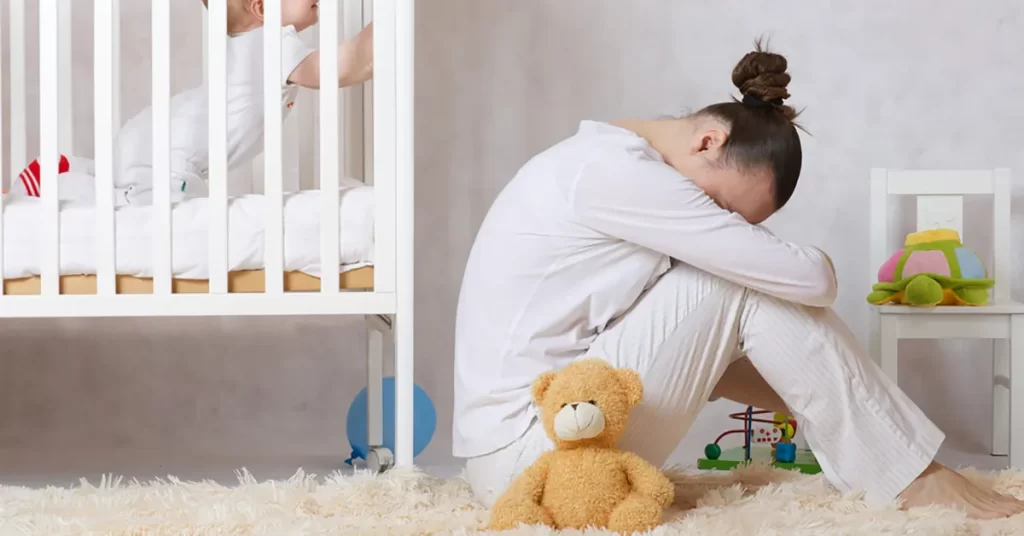
Postpartum depression (also called Postpartum Depression) is a significant mental health condition that can affect individuals during or after pregnancy. While childbirth is often associated with joy and happiness, Postpartum Depression casts a shadow over this period, bringing forth a range of emotional and physical challenges. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore Postpartum Depression in depth, from its symptoms and causes to its impact on both mothers and babies. We’ll also discuss prevention, treatment options, and how maintaining good oral health plays a role in overall well-being.
Understanding Postpartum Depression
Postpartum Depression, often referred to as Postpartum Depression, is a form of depression that emerges during pregnancy or after childbirth. It is crucial to recognize that Postpartum Depression is not the fault of the individual experiencing it; rather, it is a medical condition that requires appropriate treatment and support for recovery.
Symptoms of Postpartum Depression
Postpartum Depression manifests through a range of emotional and behavioral changes, including:
- Persistent Depressed Mood: Feeling depressed most of the day, nearly every day.
- Emotional Distress: Experiencing shame, guilt, or feelings of failure.
- Anxiety and Panic: Feeling panicked or scared frequently.
- Mood Swings: Having severe and unpredictable mood swings.
Impact on Daily Life
Postpartum Depression extends beyond emotional symptoms and can significantly affect daily life:
- Loss of Interest: Experiencing little interest in activities previously enjoyed.
- Fatigue: Feeling excessively tired and lacking energy.
- Changes in Eating Habits: Overeating or loss of appetite, leading to weight gain or loss.
- Sleep Disturbances: Having trouble sleeping or sleeping excessively.
- Cognitive Challenges: Difficulty concentrating and making decisions.
Can Postpartum Depression Affect Your Baby?
Postpartum Depression can have far-reaching effects, not only on the mother but also on the baby. It may result in:
Domestic Violence: In severe cases, Postpartum Depression may contribute to domestic violence, posing a risk to both the mother and child.
Increased Stress: Postpartum Depression can create a stressful environment for the baby, potentially impacting their well-being.
Health Complications: Babies born to mothers with untreated Postpartum Depression may experience health complications due to neglect or a stressful home environment.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of Postpartum Depression, including:
- Stress: High levels of stress in one’s life can increase the risk of Postpartum Depression.
- Preexisting Conditions: Individuals with conditions like diabetes are more vulnerable.
- Pregnancy Complications: Complications during pregnancy, such as premature birth or multiple pregnancies, can elevate the risk.
- Substance Use: Smoking and alcohol consumption are risk factors.
- Lack of Support: A lack of support from family and friends can contribute to Postpartum Depression.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing Postpartum Depression
While Postpartum Depression cannot always be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk. Counseling or therapy is particularly effective in preventing perinatal depression, including Postpartum Depression. Therapists help individuals understand their emotions, solve problems, and cope with daily life stressors.
Treatment Options
If you suspect you have Postpartum Depression, seeking help from a mental health provider is essential. Treatment options include:
Counseling: Engaging in therapy sessions to address and manage Postpartum Depression symptoms.
Support Groups: Participating in support groups with individuals experiencing similar challenges.
Medications: In some cases, antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), may be prescribed. However, the use of medications should be carefully evaluated, especially if breastfeeding.
Wellness Strategies for Postpartum Depression
In addition to seeking professional help, there are several steps individuals with Postpartum Depression can take to support their recovery:
Stay Physically Active: Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking or going to the gym.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Consume healthy foods, including fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
- Prioritize Rest: Get as much rest as possible, syncing your sleep schedule with your baby’s.
- Avoid Harmful Substances: Refrain from alcohol, sugary drinks, smoking, and vaping.
- Oral Health: Maintain good oral hygiene to prevent dental problems associated with depression.
The Impact of Depression on Oral Health
Depression can have a profound impact on oral health. It can lead to neglect of oral hygiene, poor nutrition, and dental problems such as dental caries, gum disease, and dry mouth. Furthermore, chronic stress and anxiety can lead to teeth grinding, causing damage to teeth. Managing depression and maintaining oral health go hand in hand to ensure overall well-being.
What is the primary focus of Postpartum Depression (PPD)?
Postpartum Depression is a form of depression that occurs during or after pregnancy and requires appropriate treatment.
Can Postpartum Depression affect the baby?
Yes, Postpartum Depression can have repercussions on both the mother and the baby, including increased stress and health complications for the baby.
How can I prevent Postpartum Depression?
While Postpartum Depression cannot always be prevented, certain counseling or therapy sessions can reduce the risk.